What is HAZOP?
The Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Study is a structured and systematic assessment of a complex system, (such as process facility) in order to identify the hazards that can cause potential danger to Personnel, Equipment, Environment, as well as system operability. HAZOP study is considered as primary hazard identification tool in Process safety industry.
Objective Of HAZOP Study
- The primary objective of the HAZOP study is to identify and evaluate Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) hazards caused by Process deviations/System failures/Human error. It also helps in identifying operability issues which, are not potentially hazardous, but can compromise the plant’s ability to achieve its design intent and productivity.
- The secondary Objective of a HAZOP study is to identify the deviations and make sure that there are control panels in place to protect the process. The review is carried out using Process and Instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs). HAZOP studies help identify corrective actions, such as additional controls and recommendations, to eliminate or reduce hazards.
Importance of HAZOP in Oil & Gas Industry
The Oil and Gas industry is a high-risk industry, with potential risks that can cause significant damage to Personnel, Equipment, & Environment. HAZOP analysis is thereby a valuable tool for risk management and risk assessments in the oil and gas industry.
Here’s how HAZOP analysis can be used to improve risk management in the oil and gas industry:
- Hazard Identification in new and existing processes: HAZOP analysis can be used to identify potential hazards in new and existing systems, such as pipelines, processing plants, and drilling rigs. This information can then be used to develop risk assessments and risk mitigation strategies.
- Evaluating the adequacy of safety controls: HAZOP analysis helps evaluate the adequacy of safety controls in place to prevent and mitigate risks. This information can be used to identify areas where safety controls need to be improved.
- Improving the design and operation of processes and systems: HAZOP can identify design and operational improvements that can reduce the risk of accidents. Example, a HAZOP analysis might identify the need to add additional safety controls, Modify the existing design of a process or system, or develop new operating procedures.
HAZOP study in chemical plant
HAZOP Study determines the Process Hazards which may incur sufficient damage or injury if not appropriately controlled. It is also used for determining equipment failures that would result in process failures or accidents inside the Plant which is being examined during a HAZOP Study. A HAZOP analysis is applicable to any level of an organization from a small Unit process to entire Plant
Where is HAZOP applicable?
HAZOP study procedure is applicable to every definite operational sequences in planned and existing systems. HAZOP Analysis is most effective when held during the conceptual design stage in which recommendations impacting the general design may be fabricated.
HAZOP & HAZID Difference?
HAZOP is a more structured and systematic technique. It typically involves a team of people with expertise in the process being studied using a set of guidewords to identify potential deviations from the intended design or operation. The team then assesses the severity and likelihood of each deviation, and develops recommendations for mitigating those hazards.
HAZID (Hazard Identification) is a less formal and structured technique. It typically involves a team of people with expertise in the process being studied brainstorming potential hazards. The team then assesses the severity and likelihood of each hazard, and develops recommendations for further evaluation.
| Feature | HAZOP | HAZID |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hazard identification and evaluation | Hazard identification |
| Formality | Structured and systematic | Less formal and structured |
| Timing | Typically conducted during Basic Engineering stage, Detailed engineering stage, debottlenecking stage, operational phase, can be executed at any stage in the design lifecycle of a project | Typically conducted in the early stages of a project |
| Scope | Identifies hazards in the overall design of a process facility and in the specific equipment and procedures that will be used | Identifies hazards in the overall design of a process facility |
| Output | A HAZOP report that includes a list of hazards, the severity and likelihood of each hazard, and recommendations for hazard mitigation | A HAZID report that includes a list of hazards and recommendations for further evaluation |
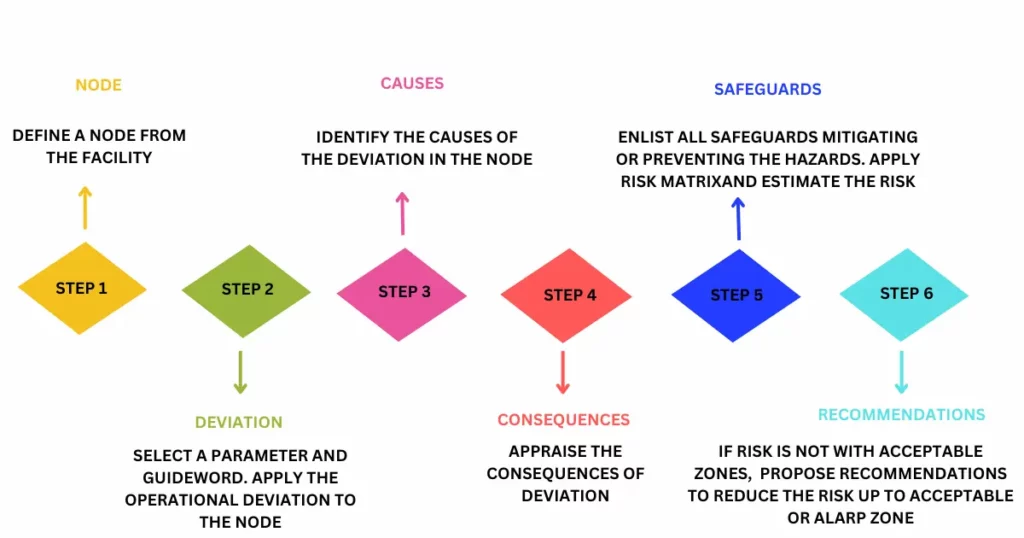
HAZOP Methodology
The HAZOP technique consists of a systematic analysis of the design in order to assess any
operability problems or process-related hazards. The HAZOP Review is developed reviewing
each P&ID using a structured step-by-step approach that allow to comprehensively analyses
the whole process via suitable guidewords, used to identify credible deviations from the design intent.
The method detects hazards and provides likely accident sequences that could occur as a result of these hazards; innovative thinking then identifies the impacts of these situations.
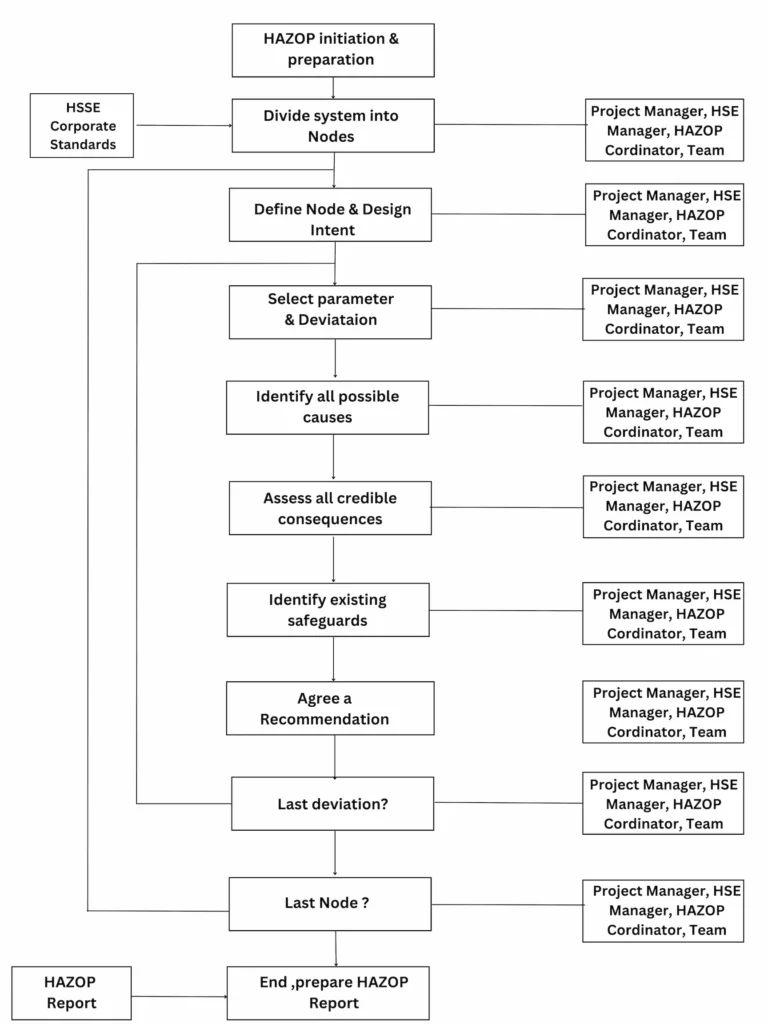
HAZOP Study Step by Step Process
The HAZOP study process typically consists of the following steps:
- The HAZOP team prepares for the study by gathering data’s about the process or system, such as Process and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs), operating procedures, and safety documentation.
- The HAZOP team identifies the nodes in the process. A node is a point or section in the process where a parameter can change. For example, a node could be a pump, a valve, or a reactor.
- The HAZOP team applies a set of guidewords to each node to generate potential deviations from the normal operation of the process or system.
- No flow: What happens if the pump fails?
- More flow: What happens if the valve overpressures?
- Less flow: What happens if there is a leak in the pipeline?
- Reverse flow: What happens if the valve flows backwards?
- Other than oil: What happens if the pipeline is used to transport a different fluid than oil?
- For each potential deviation, the HAZOP team considers the potential hazards and operability problems that could arise. If a hazard is identified, the team recommends actions to mitigate the risk.
- The team documents the results of the study, including the potential deviations, hazards, operability problems, and recommended actions in a HAZOP Report.
HAZOP Basic Rules and Assumptions
The following ground rules were set before proceeding with the HAZOP Session, and the HAZOP Chairman presented a summary at the start of the first day of the workshop:
- Equipment has been designed with adequate design envelopes for start-up, operation and shutdown;
- Equipment is designed and installed as per installation code requirements;
- Equipment and instrumentation are selected and installed compatible to local conditions;
- Double jeopardy’ failures are not considered. Common mode failures are assessed as they are considered a ‘single jeopardy’ failure;
- Flange/gasket leakages are not considered as a cause;
- Spontaneous pipe or vessel rupture is not considered as a cause;
- Single check valves are not generally considered an adequate safeguard against a hazardous backflow on their own; nevertheless, since they provide mitigation against it, they have been recorded as safeguard, when present;
- Minor changes to the P&IDs will be noted clearly on the master P&IDs in red pen, instead of recording as a recommendation at each occurrence; however, when the change is deemed to be significant, this will be also recorded in the HAZOP log sheets;
- Prolonged & side discussion shall be avoided. The objective is to identify potential hazards not to design them out during the workshop; when disagreement arises, a recommendation will be issued;
- Time will not be spent on finding solutions, unless solution is obvious;
- Sections of the existing plant will not be considered in detail; only impacts to/ from the new Project facilities to these sections will be assessed.
HAZOP Study Guidewords
The following table summarizes the main guidewords that were applied and the typical deviations obtained combining the guidewords and the process parameters.
| Parameter | Guideword | Definition |
| Flow | More Less Reverse No Other than As well as Misdirected | Quantitative Increase Quantitative decrease, includes no flow Reverse/ opposite direction Complete negation of the Design intent Complete substitution Qualitative modification/ increase |
| Pressure | More Less No | More than normal operating Less than normal operating Vacuum |
| Temperature | More Less | More than normal Less than normal |
| Level | More Less | More than normal Less than normal |
| Composition | Change Contamination | Corrosive Contamination Out of specifications |
| Others | Start-up/ Shutdown Maintenance Corrosion Utilities Failure Vent/Drain Safety | Leakage or release to atmosphere Deviations related to mentioned conditions |
HAZOP Checklist
A HAZOP checklist is a tool that can be used to identify potential hazards in a system . It is a systematic approach to examining the process and identifying any error occurring from the intended design or operation. The HAZOP team assesses the severity and likelihood of each deviation, and proposes recommendations for eliminating those hazards.
| No or None | Complete Negation (Failure of a Function) |
| More | Quantitative Increase |
| Less | Quantitative decrease |
| Reverse | Opposite of the design Intent |
| Part of | Qualitative decrease |
| AS well as | Qualitative Increase |
| Other than | Complete Substitution |
| Early/later | Relative to a clock |
| Before/ After | Relating to an order/a sequence |
| Too long/ Too late | Considering a required time |
| Too short/ Too soon | Considering a required time |
How is HAZOP Study performed?
An Online brainstorming session will be held with the multidisciplinary team accompanied by the HAZOP Chairman and Scribe. The session is led by discussion for each node, deviation, safeguards available and thereby preventive measures & recommendations will be recorded using the Software PHA Pro.
The Input documents required by the HAZOP team are as follows
- PFD’s
- P&IDs for Process & Utilities
- HSE Risk Matrix and Response Chart
- Heat and Mass balances
- Plot Plans or General Equipment Arrangements & Elevation Drawings
- Material Specifications and Selection Charts
- Cause and Effect Diagrams
- Process Design Basis
- Process Operation & Control Philosophy
- Operations and Maintenance Manual
A brainstorming session will be held onsite with the multidisciplinary team along with the HAZOP Chairman and Scribe. The session will be discussed for each node, deviation, safeguards available and mitigation measures & recommendations will be recorded with the help of software PHA Pro.
The Team indulged in HAZOP Analysis has a good knowledge of Plant Operation. Hence there wouldn’t be any chance of Field Survey as all required information can be obtained from Operating Personnel through discussions. Interviewing the Plant Operators in their working Day for few Hours will yield relevant information required to make a Hazard List which will be categorized based on frequency and Severity attributes using Checklists.
iFluids Engineering is a leading provider of HAZOP study consulting services in India. We have extensive experience working on HAZOP studies in India, Qatar, Oman, Tunisia, and many other countries. To learn more about our HAZOP case studies, please visit the link below.
Learn more about HAZOP studies with our free training and webinars. Click here
