What is HIRA?
Hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA) study offers a systematic approach to assess hazards and their associated risks. HIRA Safety helps to determine the objective of an identified hazard and provide the technique to manage the risk.
What is a HIRA risk?
It is the comprehensive process of assessment of hazards, risk examination, and risk estimation. HIRA is used to identify potential hazards in a process or system that can lead to major accidents, injuries, or environmental damage.
Once a hazard has been identified, the HIRA team will assess the severity and likelihood of the hazard.
The severity of a hazard is a measure of the potential consequences of the hazard, such as number of people that could be injured or the intensity of damage that could be caused. The likelihood of a hazard is a measure of how likely it is for the hazard to happen.
The HIRA team develops recommendations for eliminating the risk. This may involve:
- Eliminating the hazard altogether,
- Reducing the likelihood of the hazard occurring, or
- Reducing the severity of the consequences of hazard.
HIRA risks can be classified into different categories, such as:
- Process risks: These are risks that are associated with the process itself, such as the risk of fire or explosion.
- Equipment risks: These are risks that are associated with the equipment used in the process, such as the risk of equipment failure.
- Human factors risks: These are risks that are associated with human error, such as the risk of a worker making a mistake.
Why HIRA is important?
By identifying and Assessing risks, HIRA can help reduce the likelihood and severity of major Accidents, Injuries, and Environmental damages. It helps us:
- To determine all possible factors that may harm the workers.
- To determine the probability of incidents and analyzing it’s severity
- Identify the existing safeguards and controls.
- Assess the Safety risks and to make sure they are within acceptable limits.
- Suggestions to counter the likelihood of hazards
HIRA and HAZOP
HIRA and HAZOP are both hazard identification techniques used in the Process safety .
- HIRA (Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment) is a structured method for detecting and evaluating hazards in process facilities/systems. HIRA detects potential risks that may cause accidents, injuries, or environmental damage. HIRA is a simple and straightforward technique that can be used to identify dangers in a variety of operations.
- HAZOP (Hazard and Operational Study) is a more extensive and rigorous approach to hazard identification and assessment. HAZOP team uses a set of guidewords to detect potential deviations from the planned design or operation. The team then analyses the severity and likelihood of each deviation and suggest mitigation solutions. HAZOP is a more complicated and time-consuming procedure than HIRA, but it is also more thorough and effective.
HIRA and HAZOP study data can be utilized to create a comprehensive risk management plan. The risk management plan should identify Hazards, Analyze risks, and make mitigation recommendations.
Organizations can increase safety of their process facilities and reduce the risk of major accidents, injuries, and environmental damage by combining HIRA with HAZOP.
How many types of HIRA are there?
The following are the types of risk assessments, There are three types of risk assessments namely Baseline Risk Assessments, Issue-Based Risk Assessments and Continuous Risk Assessments.
- Baseline Risk Assessments:
The baseline risk assessment is conducted to identify the risk occurring at first time, Based on the outputs of the Baseline risk assessment, definite aspects or issues will be accentuated. The Baseline risk assessment should be reviewed on planned intermissions to restore the baseline profile so as to reduce HIRA Safety risks in an organization.
- Issue-Based Risk Assessments:
An Issue-based risk assessment will be conducted due to accentuated aspects or issues, occurrence of new processes, Installing new machines or the ongoing assessment of Hazard in an organization.
- Continuous Risk Assessments:
Continuous risk assessments forms a part of all inspections and observations that occurs on routine basis.
What are the 3 Phases of HIRA ?
- Phase 1: Identification of Hazard
In this phase all possible incidents are determined and catalogued. Field visit and study of all procedures related to Operations and Input documents like Drawings and Process write-up are used in identification of Hazards.
- Phase 2: HIRA Risk Assessment
Inputs Needed
HIRA is highly dependent on the availability and accuracy of the input data, When provided with complete Input data, a higher confidence on the validity and robustness of the results are obtained. The example of data collection will be specific to operations, building design, personnel / population occupancy levels.
Risk Assessment Methodology
HIRA Risk Assessment is employed for risk management and safety improvement in several industries. It provides a quantitative assessment of potential risks known and provides a basis for evaluating process safety with reference to a planned risk acceptance criterion.

The study method is a combination of identification, analysis and brain storming based on the hazards identified which is divided into four main sections containing several categories. The generally applicable categories are;
- Section 1 External and Environmental Hazard;
- Section 2 Facility Hazards;
- Section 3 Health Hazards and
- Section 4 Assess Risks to:
- People
- Asset /Production
- Environment
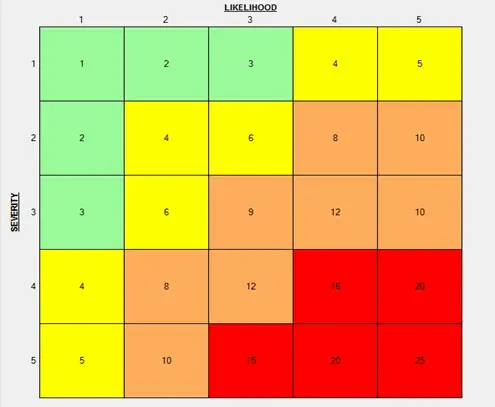
- Phase 3: Elimination of the Risk The known hazards will be listed and checked within the risk matrix to grasp the importance of risk, the safeguarding controls / measures will be described based on the risk ranks and at last the recommendation shall be provided to prevent / eliminate the potential hazards. The risk matrix used for the study is given below
Hazard Likelihood rating
| Likelihood | Description | Rating |
| Most Likely | The presumably result of the hazard/event being realized | 5 |
| Possible | Has a good probability of occurring and is not unusual | 4 |
| Conceivable | Might occur at some time in future | 3 |
| Remote | Has not been identified to occur after several years | 2 |
| Inconceivable | Is practically not possible and has never occurred | 1 |
Hazard Severity Rating
| Severity | Description | Rating |
| Catastrophic | Numerous fatalities, irretrievable property damage and productivity | 5 |
| Fatal | Approximately one single fatality or major property damage if hazard is realized | 4 |
| Serious | Non-fatal injury, permanent disability | 3 |
| Minor | Disabling however permanent injury | 2 |
| Negligible | Minor abrasions, bruises, cut, first aid type injury | 1 |
Risk Matrix
Risk Rating
| Risk | Description | Action |
| 15 – 25 | HIGH | A HIGH risk needs immediate action to manage the hazard as detailed within the hierarchy of control. Actions taken to be documented on the risk assessment form as well as date for completion. |
| 5 – 12 | MEDIUM | A MEDIUM risk needs a planned approach to manage the hazard and applies temporary measure if needed. Action to be documented on the risk assessment form as well as date of completion. |
| 1 – 4 | LOW | A LOW risk could also be considered as acceptable and any reduction might not be necessary. However, if risk can be resolved quickly and expeditiously, control measures got to be enforced and recorded. |
LSIR (Location specific Individual risk)
Location specific Individual risk (LSIR) is that the risk for a hypothetical individual positioned at particular location for 24 hours on a daily basis 365 days per year. The LSIR criteria are employed in order to produce an over view of the long run industrial land use planning and developments. This individual risk is acquired directly from the risk software’s. The LSIR derived from risk software shall be supplied with the unit of Individual / societal Risk Frequency per year.
What are the main 5 risk assessment stages?
- Determining the scope of risk assessment.
- Determining the resources needed.
- Determining the type of risk analysis measures.
- Determining the stakeholders involved.
- Determining appropriate regulations or standards applicable as per Organizational policies
