Assam Gas Company Ltd., a Govt. of Assam Undertaking was incorporated on March 31, 1962 in Shillong as a limited company wholly owned by the Government of Assam to carry out all kinds of business related to natural gas in India. It has its present headquarters in the oil town of Duliajan in the district of Dibrugarh, Assam, India. The Company can transport over 5.5 MMSCMD of natural gas. Over the years, AGCL has established branch offices in 14 different locations in Assam.
Assam Gas Company Limited has awarded iFluids Engineering to carry out a Quantitative risk assessment (QRA) study , Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) , & EMERA (Escape, Muster, Evacuation, and Rescue) study for the CNG mother station at Duliajan & Hazarigaon, Assam.
FACILITY DESCRIPTION:
Hazarigaon station has the following facilities,
- METERING SKID (1 no, Capacity- 1200SCMH)
- RECIPROCATING GAS COMPRESSOR (1 no, Compressor Capacity – 1200 SCMH)
Duliajan station has the following facilities
- METERING SKID (1 no, Capacity- 2400SCMH)
- RECIPROCATING GAS COMPRESSOR (2 nos, Compressor Capacity – 1200 SCMH)
PROCESS DESCRIPTION:
The CNG station is classified into the following categories:
- Online stations
- Mother Stations
- Daughter Booster Stations
- Daughter Stations.
CNG Stations
The CNG Stationis a Station that receives CNG through the pipeline of 19 – 22 kg/cm2g or mobile cascade from nearby mother stations above 250 Kg/cm2g. After getting compressed via the compressor, the gas would be sent to Dispensing Units (DU) and Cascade in Online and Mother stations. And the compressed gas at 250 kg/cm2g would be sent to Dispensing Units (DU) to Daughter Booster stations. Also, the gas would be sent to Dispensing Units (DU) without compression in Daughter stations which is mentioned in the below figures.
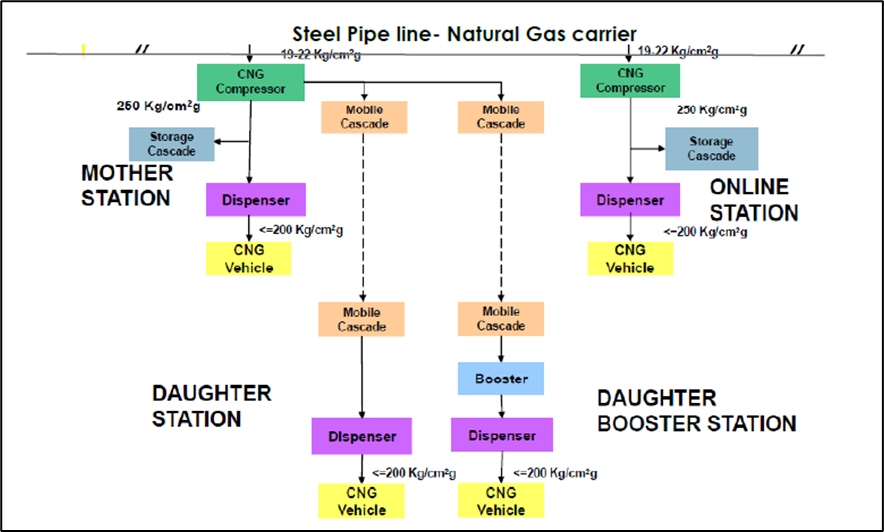
Daughter Booster Stations:
Daughter Booster Stations are equipped with Booster Compressors and station cascade including Priority Panel. This arrangement helps to unload more than 75% of the incoming LCV Cascade volume for dispensing.
CNG is dispensed to vehicles based on the principle of pressure equilibrium. Once the pressure of a mobile cascade drops below 200 bars at daughter stations, vehicles get less amount of gas, which is below 200 bars. With each fill thereafter, the amount of gas dispensed to vehicles starts decreasing and the filling time starts increasing, thereby leaving the customer dissatisfied.
Daughter booster stations address the issue. These are similar to daughter stations. However, to cater to customers concerning the amount of gas dispensed as well as filling time, a booster compressor (the hydraulic type with variable suction pressure) is installed in between the mobile storage and the CNG dispenser. The booster compressor increases the pressure above 200 bars once the pressure of the mobile cascade falls below 200 bars. Thus, the maximum amount of gas stored in the mobile cascade is dispensed to the daughter booster station.
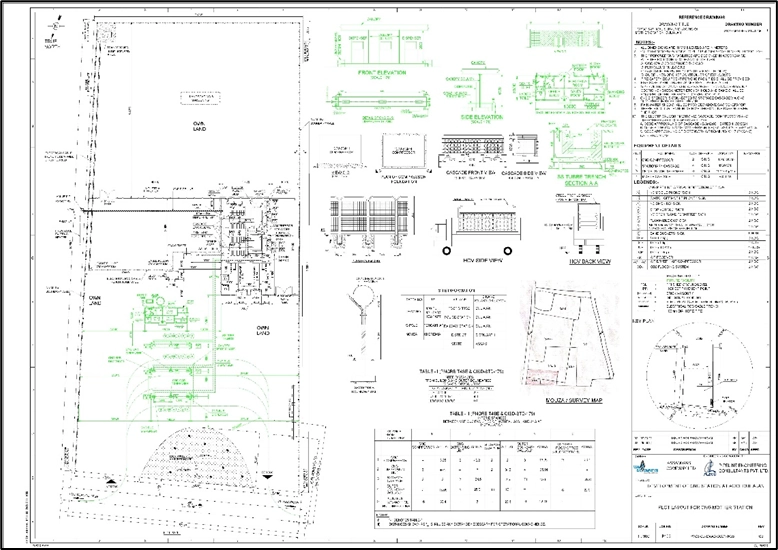
Overall Layout- Duliajan
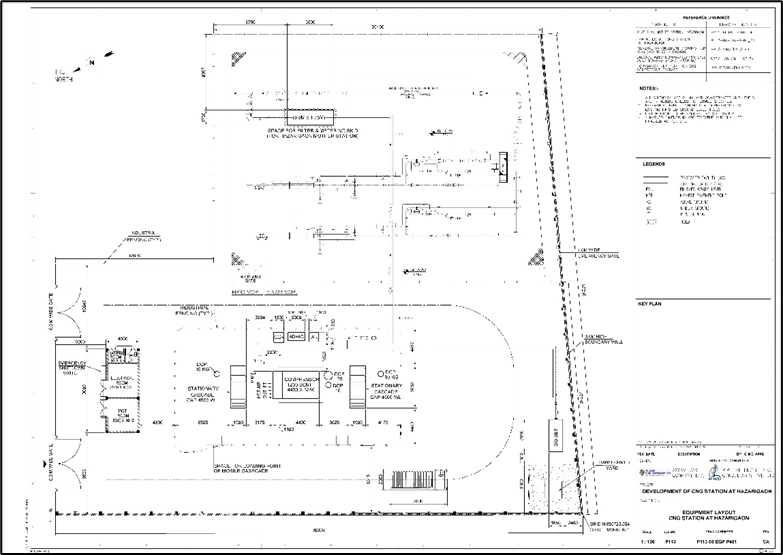
Overall Layout- Hazarigaon
HAZOP STUDY
The main objective of the HAZOP study is for early identification of hazards that are associated with the process and operation and to reduce the probability and lead consequences of an incident that would have a detrimental impact on humans, facilities, properties, and the environment.
The Objectives of HAZOP are as follows:
- To identify the hazards which are associated with the Process and Operation.
- To identify the credible causes such as manual/equipment/instrument failures likely to lead to hazards.
- To qualitatively assess the risk (L/M/H/S) and provide recommendations to prevent/overcome the hazards if required which will be assessed using the qualitative judgmental of the likelihood and consequence rank of an incident.
- In addition to these issues, HAZOP occasionally identifies items that could improve unit operations and the efficiency of the process.
QRA (Quantitative Risk Assessment)
The assessment will be based on the hazards that may occur during the operations of the project according to the information available. The scope of work is limited to the different components associated with the proposed facility only. Any other facilities that are not part of the proposed complex operations are not included as part of this study. The following facilities are covered under the QRA study for the Project.
- Mobile cascade (2 Nos.)
- Booster Compressor and Stationary Cascade (2 Nos.)
- Dispenser (1 No.)
Objective of QRA
The main objective of this study is to evaluate the potential risk levels for personnel due to the accidental release of hazardous materials from loss of containment scenarios from the facilities and to demonstrate that individual risks are within the broadly acceptable regions.
The Objectives of QRA are as follows:
- Identification of Hazards and Major Loss of Containment (LOC) events
- Calculation of physical effects of failure case scenarios which include Estimation of Jet Fire, Pool Fire heat radiation distances, Flammable gas dispersion distances, and overpressure explosion distances
- Failure Frequency evaluation
- Societal risk quantification and Potential Loss of Life estimation
- Perform a risk assessment to confirm that risk can be reduced consistent with the ALARP principle according to the UK HSE risk acceptance criteria
- Recommend risk-reducing measures to ensure that all risks are in ALARP or Acceptable region.
EMERA (Escape, Muster, Evacuation, and Rescue)
The adequacy of Escape, Muster, Evacuation, and Rescue systems will be assessed according to the information available. The scope of work is limited to the different components associated with the proposed facility only. Any other facilities that are not part of the proposed operations are not included as part of this study. The following facilities are covered under the EMERA study for the Project.
- CNG Filling station- Duliajan
- CNG Filling station- Hazarigaon
Objective of the Escape, Muster, Evacuation, and Rescue Analysis (EMERA
The objective of the Escape, Muster, Evacuation, and Rescue Analysis (EMERA) is to systematically address the effects of accidental events on the adequacy and the availability of Escape, Muster, Evacuation, and Rescue (EMER) systems and to perform their intended functions. The study will cover the following:
- Escape routes analysis – Each area in the facility is to be assessed in terms of provision of escape provisions following OGP guidelines.
- Evacuation time analysis – The objective of the evacuation time analysis is to assess if the assembly area and evacuation facilities can endure fire events for the period required for the personnel in the plant to evacuate;
- Evacuation provision analysis – To check for adequate provision of the evacuation facility, such that all personnel could safely evacuate the facility when required; and
- Rescue provision analysis – To assess the provision of rescue facilities for suitability and adequacy.
- Provide suitable recommendations for the impaired escape routes.
