What is the Bow Tie Model ?
A ‘Bow-Tie’ is a graphical representation of the pathways from the causes of an event or risk to its consequences. The diagram is shaped like a bow-tie, creating a clear differentiation between reactive risk management and proactive
How does Bow Tie Analysis work?
Bow tie analysis is of mostly used for risks that pose elevated levels of risk, and specifically those with high consequences. It describes the risk as some happenings that subsequently leads to a consequence.
Approach / Methodology
The bow-tie diagram helps you to gain an insight in complex processes through oversight. This objective is always leads ahead of others and can therefore overrule the guidelines if necessary. The objective to keep an understandable diagram always over weighs the intention to be analytically correct.
There are eight basic steps in building a bowtie diagram. They are as follows:
- Identify hazard: – The first step in managing risks is to identify what their sources are.
- Identify top event:-When we know what is potentially hazardous, we need to know how we could lose control over it.
- Identify threats: – Next we need to consider the scenarios or events which could directly cause the occurrence of the top event.
- Evaluate consequences:-After the top event occurs, subsequent scenarios or events are now possible. These consequences can lead to losses and damage.
- Identify preventive barriers:- The next step is to identify the barriers which should prevent the threats from reaching or causing the top event. These are preventative barriers.
- Identify recovery barriers:-Barriers on the right side try to recover from the occurrence of the top event. These barriers should prevent or alleviate the consequences and/or the resulting losses and destruction.
- Identify escalation factors: – The next step is to identify the specific situations or conditions under which the barriers are less or not effective.
- Identify escalation factor barriers:-The last step is to look at what barriers you have to prevent or manage these escalation factors.
Now with the escalation factors in place, our complete diagram is as follows:
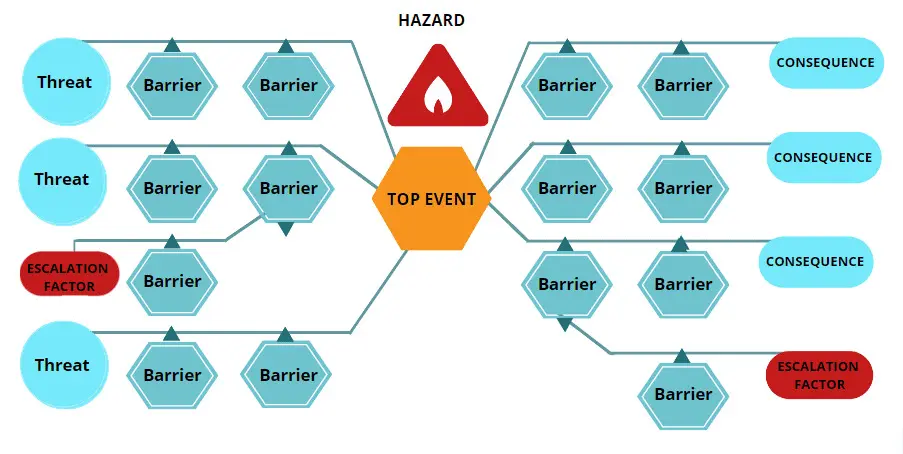
Figure: Complete Bow-tie Diagram
Now the diagram can be completed with more information over each barrier:
- Determining the barrier type.
- Which parts of the management system support the barrier, such as procedures, policies, standards, etc.?
- Who is responsible for the correct functioning of each barrier?
- Assessing barrier effectiveness.
This study is done by a team which usually comprises of the following:
- Design consultant / Project Manager
- Production Manager
- Chemical engineer / Chemist
- Maintenance Manager
- Electrical Engineer
- Instrument Engineer
- Quality Control Engineer
- HSE Representative, etc.
Within the team, a lead facilitator should be nominated to lead the study. The lead facilitator should be a competent and experienced person in the conduct of the Bow-tie study.
How do you use a Bow Tie Risk assessment?
Step 1
Bow Tie Risk assessment starts in between the hazard and the Event that you are looking to examine. It shall be written in simple English language to ensure that everyone understands what they are trying to examine.
Step 2
To the left hand side plot the potential causes or threats that will lead to the event happening, This would span things that are almost certain to happen to things that are not sure to happen.
Step 3
To the right-hand side plot all the consequences that would occur if the event associated to the hazard was to occur, and so there will be a span of them to consider.
Step 4
Go through the logical flow of the chart and think about the potential threat that happens, then this event associated with the hazard may happen and the consequences plotted may happen. If that is logical, then you have things set right, if you doesn’t feel right then it’s not a actual cause or consequence.
Now counter measures or Controls & Mitigation steps can be initiated.
Step 5
Starting on the right hand side, for each cause what control measures could be initiated so as to prevent the particular possible cause from occurring. Many controls can be initiated for each cause to avoid it from happening. For each control it can be ranked as High risk, Medium risk, or Low risk based on its effectiveness in being able to prevent the possible cause from happening.
Step 6
Repeat the process at the right-hand side, with the preventive steps that can be had if the event occurs and that will eventually restrict or stop the possible output or consequences from being impacted.
Step 7
For each Controls and preventive steps it is necessary to add the safety critical actions that needs to occur to support them. To ensure that the control and preventive measures in demanding situations, the following should be practiced in Policies, Procedures and Job description
- The actions to be taken to keep the control or preventive measures happening
- The Concerned person to do these actions.
Step 8
In this Final Step review and find the listed equipment. As these items are safety critical equipment. Prioritize based on their Function, performing capability, availability, and survivability.
Bow Tie Risk Analysis example
A hazard is something that is able to intend harm or initiate an Event, for that to occur something must happen to permit the hazard to happen and the event take place. For instance a glass plate placed on the top most shelf shall be the hazard, the event is that the glass plate falls from the shelf, the threat or the thing that could cause shall be something striking the shelf making it to wobble, As a consequence it drops upon someone or something, and also it damages everything in the Glass plate and so on.
What is the advantages of using the Bow Tie Assessment?
The advantages of Bow-Tie assessment include, but not limited to:
- Provides a structure to analyze a hazard systematically.
- Helps make a decision to check the current level of control is sufficient (or, for those who are familiar with the concept, whether risks are As Low as Reasonably Practicable or ALARP).
- Helps to identify where and how investing resources would have the greatest impact.
- Increases risk communication and awareness.
What is a Bow Tie Barrier model?
Barriers appear on both sides as top event. Barriers on the left side break in the situation so that the threats does not happen, and if it happens, they do not result in loss of the top event. Barriers on the right side ensures that if the top event is attained, the situation does not surge into an actual effect such as consequences and/or they prevent the effect.
There are various types of barriers, that are mainly a mix of human behavior, with or without the interference of hardware and technology. When the barriers are detected, a common understanding of how risks are tackled is obtained. Analyze the barrier structure to identify the strength and weakness. For barrier effectiveness, Barriers can be categorized and evaluated. As this makes us understand how efficiently a barrier conducts, or is expected to conduct, depending on available data and/or depending on judgment. Later, all activities mentioned can be analysed, to implement and sustain the barriers. This eventually means mapping the Safety Management System with the Barriers. Also it can be decided about the concerned person responsible for a barrier and evaluate the criticality of a barrier based on other related information.
Technical Challenge:
It is not enough to simply identify risks they must also be managed, analysed, evaluated, monitored, and communicated to be managed: analyzed, evaluated, monitored and communicated. Bow-Tie risk management is a scenario-based management tool which helps Process Safety M to accomplish these tasks and to answer questions like: “Where we are most exposed to risk?”, “are we equipped with enough (or too many!) Safety measures in place?”, “are our safety measures actually performing the way we have in view?”
This is a risk assessment method. The bow-tie method helps to analyze and communicate how high-risk scenarios develops.
Software Requirement
Bow-Tie XP is the widely used risk assessment software based on Bow-Tie method.
Deliverables
- Bow-Tie ToR
- Bow-Tie Worksheets
- Bow-Tie Analysis Report
