What is Safety Audit?
A Safety audit is an organized process which is used to gather information associated to a company’s safety, reliability, effectiveness, and efficiency. An auditor will examine the, work environment, processes, the state of equipment, and other details to measure these qualities. In Safety audits the auditors will explore the company’s safety documents to assess how they can refine their processes and safety management systems.
Safety Audit in Industries as per IS 14489?
IS 14489 is the Risk Management tool on Occupational Safety and Health Audit. This standard demonstrates Audit objectives, criteria and practices and provides instructions for establishing, conducting, planning and documenting of audits on occupational safety and health systems of an Organization.
Safety Audit and its types
There are three types of Safety audits.
1. Compliance Audit.
The compliance audit is conducted to inspect whether the Organization acts in accordance with all the related safety laws, safety standards, and other provisions.
It can be done by Government safety inspector or other external safety auditors. This depends on Country’s safety rules, safety management system, etc.
2. Program Audit.
The safety auditor will inspect for the safety program execution that the Organization has planned or is a obligatory program put down by the Government or other parties.
3. Safety Management System Audit.
This is an overall audit, where the compliance and program will be conducted simultaneously, apart from inspecting the safety management system itself.
Why is Safety Audit important?
Safety Audit is very important under various regulations in India. As per Section 7A of Factories Act, 1948, it becomes evident that by carrying out a safety audit and doing the necessary monitoring/follow-up, most of the obligations under this section are fulfilled.
Safety Audit is extremely important under numerous statutes in India. The overall duties of the occupier specific under Section 7-A of the Factories Act, 1948, it become apparent that by under a security audit and doing the required monitoring/follow-up, most of the obligations beneath this section area unit consummated.
Safety Audit it’s utmost necessary for the aim of maintaining safety (accident free atmosphere) in business that all system of work should be thoroughly checked from safety point of view at regular interval and deficiencies known should be removed by due compliance of safety recommendations.
Normally an external or third party safety audit ought to be conducted once in year and an internal audit is also organized in each 6 month.
What is Safety Audit checklist?
A Safety Audit checklist is an instrument which will help to assess the safety conditions and practices in any workplace in compliance to usual safety standards and regulations. It lists the safety basis to be reached in order to address compliance gaps, and impart opportunities to enhance the workplace ambiance
Safety Audit checklist is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that you can use and amend to meet your definite needs. It can easily be amended to incorporate extra checklist items based on existing work ambiance, as it was particularly designed for manufacturing operations. It is divided into two different parts; one that is made for operational workplaces in general, and the other that is used for the construction and manufacturing activities.
Difference between Safety Audit and Safety Inspection
Safety Audits assess whether programs and procedures are meeting a company’s objectives. Whereas, Safety inspections look for risks, hazards, and other gambits that would abstain an Organization from functioning safely. Both are important modules of an Organization’s safety plan.
Safety Audit Examples
The following are few Examples of Safety Audit with their Safety Audit Checklist.
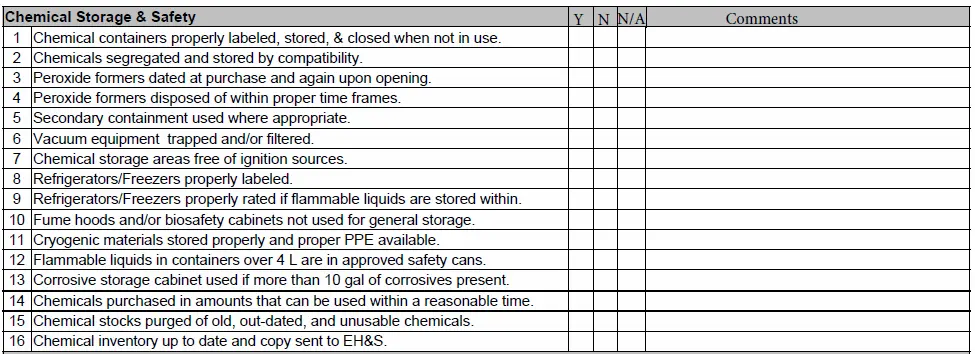
Chemical Storage Facility.
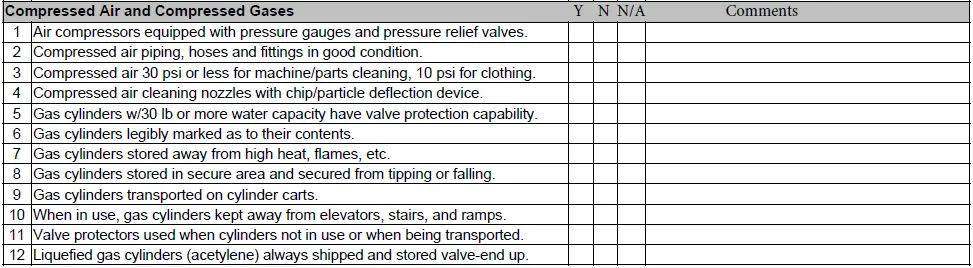
Compressed Air and Compressed Gas Facility.
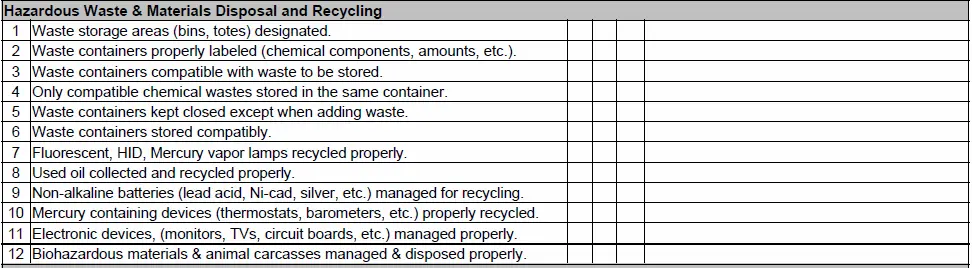
Hazardous Waste Disposal and Recycling Facility.
What is an Audit Scope?
The scope and depth of the audit needs be set as per auditee’s or client requirements. This could include:
- Which plants or areas to be audited.
- Which OS&H system components to be audited.
- With what legal and alternative safety standards, rules or documents, the auditee’s OS&H systems ought to be compared. Benchmarking if any, should be thought-about.
- List of resources and evidences together with staff and specialists that will be accessible for audit.
- Within what timeframe audit should be completed and with what alternative terms and conditions. An understanding, if necessary, written agreement be prepared and signed.
Safety Audit Procedure:
Audit arrangements should be finalized once consulting the Auditee and a plan to execute the Audit should be circulated to Auditors and Auditee in the opening meeting. This arrangement ought to include:
- Audit goals, objectives and scope of the Audit.
- Name of audit team members and managements representatives.
- List of documents to be checked.
- List of legal and alternative standards to be followed throughout Audit.
- Auditee’s OS&H policy and its alternative intentions.
- Time schedule of audit visits of each plant or location.
- Schedule of meetings to be held with auditee for the audit purpose.
- Expected date of issue of the Safety Audit Report.
- Procedure or methodology of compliance of the Safety Audit report.
Whether compliance audit will be required by the Auditee and if yes, its probable time schedule, and method of communication
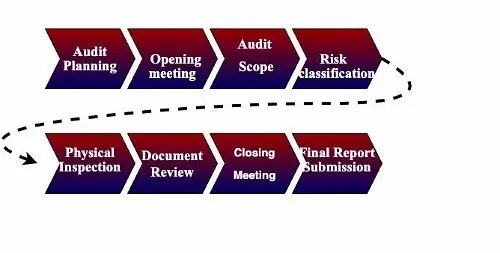
Audit Techniques – How to conduct safety audit?
To carry out an effective audit, three key procedures should be followed:
Document Assessment: The documents that should be assessed include: Safety plan, training reports, Incident reports, Health and Safety policy, Emergency plan, etc.
Interviews: Interviewing the key personnel in the organization, and random interviewing of employees would also be useful.
Workplace observation: Walking around the Workplace to have a first-hand observation. This observation can be based on compliance.
The audit procedures follow five simple steps:
- Preference for audit: Here you can confirm who will conduct the audit, Also we get to know the objective of the audit, An insight to review the applicable standards, and to refer the results of previous audit.
- Conducting the Audit: As mentioned in the Audit Techniques above.
- Creating an Audit Report with recommendations: The Safety Audit report should mention the findings. The Report shall mention both Positive findings and negative findings. The outline of the Safety Audit Report should suggest actions in areas that require improvement.
- Set Priorities for corrective action: Suggested actions should be prioritized with respect to execution time, as some may need immediate actions whereas others may not require immediate actions.
- Publishing the Audit Result: The recommendations and corrections shall be acceptably communicated. Since this act may make everyone to perceive the required changes and make them discern how these changes would impact them and their work.

Safety audit is an elaborated and organized process. iFluids Engineering helps to supply competent, experienced, certified Auditors team to clients as per your custom-made need for various types of Audit requirements & deliverable.
