GAIL (India) Limited awarded iFluids Engineering to carry out Quantitative and Qualitative Risk Assessment (QRA) study for their 278 km long Cross country Pipeline in Cauvery Basin. The scope of study is to systematically identify the potential hazards associated with GAIL pipelines, respective terminals and SV stations through risk assessment methodologies.
Brief on Client and the Location-specific details
GAIL (India) Limited was incorporated in August 1984 as a Central Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) under the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas. It is the largest state-owned natural gas processing & distribution company.
Pipeline Specification details and what it transports
- Cross country pipelines of 278 km of diameters 4,6,8,12,18 inches
- Isolation valves – Manually, Remotely or Automatically activated
- Relief valves – Pressure or Thermal
- Casing sleeves under Road / Rail crossing
- Leak Detection system
- Pig launchers Receivers
LIST OF STATION/INSTALLATIONS (RISK ANALYSIS) AT CB PIPE LINE NETWORK
- Dispatch Terminals/Gas Collecting Station
| Sl No | Station Name | Location | Gas Supplier Name |
| 1 | NANNILAM GCS | NANNILAM GCS | ONGC |
| 2 | KAMALAPURAM GCS | KAMALAPURAM GCS | ONGC |
| 3 | ADIYAKKAMANGALAM GCS | ADIYAKKAMANGALAM GCS | ONGC |
| 4 | TIRUVARUR EPS | TIRUVARUR EPS | ONGC |
| 5 | NARIMANAM GCS | NARIMANAM GCS | ONGC |
| 6 | NALLUR EPS | NALLUR EPS | ONGC |
| 7 | KUTHALAM GCS | KUTHALAM GCS | ONGC |
| 8 | AKM – MEMATHUR | AKM – MEMATHUR | ONGC & HOEC |
| 9 | RAMNAD (VALANTHARAVAI) GCS | RAMNAD (VALANTHARAVAI) GCS | ONGC |
| 10 | BHUVANAGIRI GAS DESPATCH TERMINAL – ONGCL | BHUVANAGIRI GAS DESPATCH TERMINAL – ONGCL | ONGC |
- Sectionalizing Valve station
| Sl No | Station Name | Location | Maintenance Base |
| 1 | SV-1 MARAKKANCHAVADY | Marakkanchavady | NARIMANAM |
| 2 | SV-2 THIRUMARUGAL | Thirumarugal | NARIMANAM |
| 3 | SV-3 MEMATHUR | Memathur | KUTHALAM |
- List of Gas RT/CT in Cauvery Basin Pipeline Network
| Sl No | RT/CT | Maintenance Base |
| 1 | CHENNAI PETROLEUM CORPORATION | Narimanam |
| 2 | KIRAN SILICATE (P) LTD | Narimanam |
| 3 | NANNILAM SILICATE (P) LTD | Narimanam |
| 4 | EZHIL CHEMICALS (P) LTD | Narimanam |
| 5 | SUNDRISE SILICATE (P) LTD | Narimanam |
| 6 | MADRAS CHEMICALS (BOOTH) | Narimanam |
| 7 | REENA SILICATE IND. (P) LTD | Narimanam |
| 8 | SREE JAYADEVI INDUSTRIES | Narimanam |
| 9 | PREM CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | Narimanam |
| 10 | PONDY CHEM (P) LTD | Narimanam |
| 11 | SILICATE INDIA | Narimanam |
| 12 | HENKEL SPIC INDIA LTD | Narimanam |
| 13 | H&R JOHNSON | Narimanam |
| 14 | KOTHAVARI SUGARS & CHEM. LTD | Narimanam |
| 15 | R.J. CHEMICALS | Narimanam |
| 16 | BOSS PROFILES LIMITED | Narimanam |
| 17 | REGENCY CERAMICS LIMITED | Narimanam |
| 18 | SOUNDARARAJA COTTON MILLS | Narimanam |
| 19 | MMS POWER | Narimanam |
| 20 | MURUDESHWAR CERAMICS | Narimanam |
| 21 | GODREJ SARA LEE, TIRUNALLAR | Narimanam |
| 22 | ADITYA FERRO ALLOYS | Narimanam |
| 23 | KAMAKSHI CHEMICALS | Narimanam |
| 24 | KARAIKAL INDUSTRIES | Narimanam |
| 25 | VAIGAI INDUSTRIES | Narimanam |
| 26 | GODREJ SARA LEE, NEDUNGADU | Narimanam |
| 27 | CHEMPLAST SANMAR | Narimanam |
| 28 | PONDICHERRY POWER CORP. LTD | Narimanam |
| 29 | VANJUR SILICATE | Narimanam |
| 30 | RAGHAVENDRA ALKALIES | Adiyakamangalam |
| 31 | DIAMOND SILICATE | Adiyakamangalam |
| 32 | NARIMANAM SILICATE | Adiyakamangalam |
| 33 | SOUTHERN REFRACTORY | Adiyakamangalam |
| 34 | TNCSC, TIRUVARUR | Adiyakamangalam |
| 35 | SOUTH INDIA EDIBLE OIL PVT.LTD | Adiyakamangalam |
| 36 | TNEB (TIRUMAKKOTTAI) | Adiyakamangalam |
| 37 | PREM CHEMCO | Adiyakamangalam |
| 38 | TNEB POWER | Kuthalam |
| 39 | ABAN POWER | Kuthalam |
| 40 | OPG ENERGY | Kuthalam |
| 41 | SAHELI EXPORTS | Kuthalam |
| 42 | KAVERI GAS POWER | Kuthalam |
| 43 | TNEB (VALUTHUR) | Ramnad |
| 44 | COROMANDAL ELECTRIC | Ramnad |
| 45 | ARKAY ENERGY | Ramnad |
| 46 | ARKAY ENERGY (RAMESWARAM) | Ramnad |
| 47 | SAI REGENCY POWER CORP. | Ramnad |
| 48 | NEYCER TERMINAL (VADALUR) | Bhuvanagiri |
What is Quantitative Risk Assessment?
Quantitative Risk Assessment is a systematic approach to spot hazards, evaluate the danger & include appropriate measures to manage and mitigate risk for any work process or activity, In this method, the evaluated/estimated risk is quantified numerically.
What is Qualitative Risk Assessment?
Qualitative Risk Analysis involves identifying threats (or opportunities), how likely they’re to happen, and therefore the potential impacts. Qualitative Risk Assessment is administered by Risk Index Method. In this method, the evaluated/estimated risk is described in words (Low, Medium and High as per the danger assessment criteria).
Risk Index Method
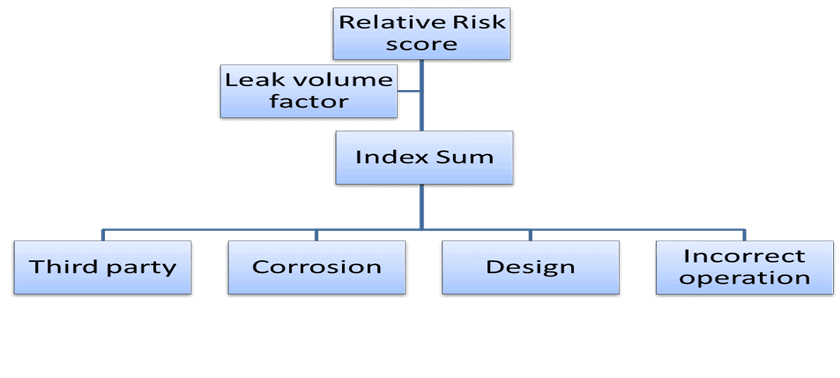
The risk factor is an important parameter that determines the ways to develop a Risk Assessment model, using either a data first or a frame first model. Since pipelines usually go across many regions whose conditions vary significantly, it is important to have a complete and universally accepted list of factors that can be used to build a risk assessment model. Risk assessment model parameters viz. Third-Party, Corrosion, Design, and Incorrect Operation would then be summed up and multiplied by the leaked impact (based on Product Hazard, Dispersion, Leak volume, and Receptors) shall be used for assessment of the pipeline integrity
Why Risk Assessment is carried out for pipelines?
Risk Assessment of the pipelines is conducted to identify the location-specific events or conditions, or combination of events and conditions that could lead to loss of pipeline integrity, and provides an understanding of the likelihood and consequences of these events.
This identification of location-specific risks were carried out in consultation with GAIL after analyzing the data like Pipeline routing drawings, mechanical data, CP (Cathodic Protection) data, construction details, historic leak /rupture data, O&M philosophy etc. Which was provided by GAIL. These risks shall be rated as Low, Medium and High as per the risk assessment criteria.
PNGRB guidelines represent 22 root causes for the threat to pipeline integrity. One of the cases reported by the operator is “unknown”. The remaining 21 threats have been classified into three groups based on time dependency and further into nine categories of related failure types according to their nature and growth characteristic as shown below
Time Dependent threat
1. External Corrossion
2. Internal Corrosion
3. Stress Corrosion
Stable Threats
- Manufacturing related defects.
4.Defective pipe seam
5.Defective pipe
- Welding / fabrication related
6. Defective pipe girth weld
7. Defective fabrication weld
8. Wrinkle bend or buckle
9. Stripped threads /broken pipe /coupling failure
- Equipment
10. Gasket O-ring failure
11. Control/relief equipment malfunction
12. Seal pump packing failure
13. Miscellaneous
Time Independent Threats
- Third party / mechanical damage
14.Damage inflicted by first, second or third party (instantaneous /immediate failure)
15. Previously damaged pipe (delayed failure mode)
16. Vandalism
17. Rat bites
18. Electric Arching 19. Weather related and outside force
- Weather related
- Lightning
- Heavy Rains or Floods
20. Earth Movements
21. Incorrect operational procedure
Risk Assessment Methodology
The Risk Assessment Study includes the following steps:
- Initial Data gathering, review and validation
- Identifying potential threats to the integrity
- Relative Risk Scoring Based Pipeline Risk Management Manual
- Consequence and impact Analysis
- Estimation of Risk assessment from total failure frequencies
- Classification of pipelines based on risk
- Integrity Assessment
How to evaluate the residual life to minimize failures and sustain pipeline operations.?
Following test methods as per OISD -SOP- Integrity assessment of Petroleum and Natural Gas Pipelines should be performed for pipelines crossing 25 years of design life to assess the health of the pipeline :
- Feed Quality Analysis w.r.t. CO2, H2S, Cl, S, moisture/water, condensate, pH value etc.,
- Scrapper pigging
- Pig residue analysis Record of quantity and quality of deposits (pig residue) collected after descaling shall be examined to monitor the condition of the Pipeline w.r.t. Fe, Fe2O3, Si, S, H2O, pH value, SRB, sulphates, carbonates, etc.,
- Internal Corrosion Monitoring
- Intelligent Pigging Survey
- Regular line patrolling
- Inspection of the leak detection system
- Inspection of communication and control system
- Pressure testing (Hydro testing)
- Risk assessment
- Fatigue Testing (for ERW and LSAW pipes)
- Design conformity Test
- Coating survey (CAT/ DCVG/CIPS)
- Soil Testing
- Cathodic protection, monitoring, upgrading and effectiveness testing
Software Used:
DNGVL PHAST SAFETI 8.22
Recommendations
The Recommendation is done as per the OISD Standards and best Engineering practices
